SEO
Brightspot gives editors the ability to characterize their content such that search engines can more easily find it and list it in search results.
This section explains how to configure SEO fields in Brightspot CMS.
SEO overview
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of characterizing an asset so that search engines can easily find and list it in search results. While individual search engines have their own methods for finding and listing assets on the Internet, they all generally look for specific tags within the <head> element.
<title> and <meta> tags
SEO text often appears in the <title> and <meta> tags.
1<head>2①<title>Brightspot's mission is to transform the way content is created and presented.</title>3②<meta name="description" content="Brightspot gives you all of the tools you need to easily drive your brand storytelling."/>4</head>
- ①Shows SEO in the
<title>tag. - ②Shows SEO text in the
<meta description>tag.
Open Graph properties
SEO text often appears in Open Graph Tag properties used by social networks.
1<head>2①<meta property="og:title" content="Brightspot's mission is to transform the way content is created and presented">3②<meta property="og:url" content="https://brightspot.com/brightspots-mission-is-to-transform-the-way-content-is-created-and-presented">4③<meta property="og:description" content="Brightspot gives you all of the tools you need to easily drive your brand storytelling forward and transform your digital customer experiences—without compromise">5④<meta property="og:site_name" content="Brightspot">6⑤<meta property="og:type" content="article">7</head>
- ①Specifies the asset's title when appearing in a social network.
- ②Specifies the URL to which visitors arrive after clicking on the link in a social network. For example, if Malcolm shared an item on his Facebook page, Facebook includes this URL in the share. When Amy clicks on the shared item, she arrives at this URL.
- ③Shows the tag line appearing in a social network.
- ④Specifies the site name to display in the social network.
- ⑤Specifies the type of asset.
How Brightspot populates SEO text
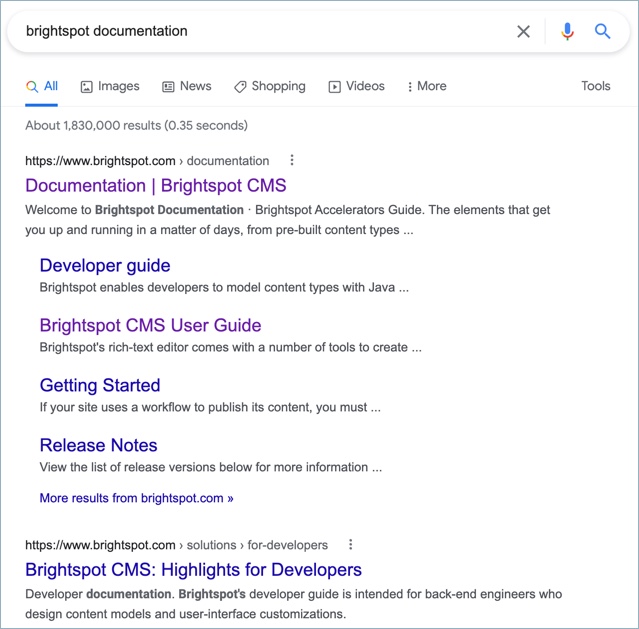
Depending on the asset you create, Brightspot automatically populates the SEO fields. For example, text you type in Headline and Subheadline fields automatically appears in the Title and Description fields under the SEO tab.
You can add or modify an asset's SEO entries as described in the section on configuring SEO for an asset below.
How search engines use SEO text
Generally speaking, when a search engine lists your asset in search results, the text it displays comes from the <title> and <meta description> tags—which Brightspot populates from your entries in an asset's SEO tab. In addition, Google sets the search terms in boldface.
Configuring sitemap generation
A sitemap is a special file on your site that improves search-engine optimization; it gives indications to search engines regarding all of the published assets on your site, when they were last modified, and other metadata. When you provide a sitemap to search engines, they potentially provide more accurate and timely results—and more click-throughs to your site.
Brightspot generates a default sitemap file sitemap.xml which you can manually submit to search engines or specify in your sites' robots.txt files. This topic explains how you can customize the sitemap's generation.
To configure sitemap generation:
- Click > Admin > Sites & Settings.
-
To initiate generation of sitemap files, do the following:
- In the Sites widget, select Global.
- Expand CMS > Advanced, and in the Default Task Host field, enter the name or address of the host where the sitemap background tasks will run.
- Click Save.
-
If you want to configure generation of sitemap types for all sites, do the following:
-
In the Sites widget, select Global.
-
Under Front-End, expand Sitemap Settings.
-
From the Site Map Types list, select the sitemap types you want to generate.
- News—generates sitemap entries for blog posts, articles, and press releases.
- Video—generates sitemap entries for videos.
- Standard—generates sitemap entries for all other content types.
-
-
If you want to configure sitemap generation for a particular site, do the following:
- In the Sites widget, select the site for which you are configuring a sitemap.
- Under Front-End, expand Sitemap Settings.
- From the Site Map Types list, select the sitemap types you want to generate. See the descriptions in step 5.c.
- In the Site Map Default URL field, enter set the sitemap's default URL. If you enter
https://brightspot.com, Brightspot creates a sitemap athttps://brightspot.com/sitemap.xml.If blank, Brightspot creates a filesitemap.xmlat the URL in the field Main > Default Site URL.
-
Click Save.
See also:
- Customizing a site's robots.txt
- News sitemaps
- Video sitemaps and alternatives
- Submit your sitemap to Google
Customizing a site's robots.txt
A robots.txt file provides crawling guidance to search engines, such as the following:
- Which user agents are allowed to crawl or not crawl
- Which URLs to crawl or not crawl
- Locations of sitemaps
- Limiting the frequency of crawling
Properly configuring your site's robots.txt enhances search-engine optimization.
Brightspot provides a default robots.txt with the following directives:
1User-agent: *2Crawl-delay: 10
Brightspot creates the file robots.txt at the location in the field Main > Default Site URL. For example, if your site's default URL is https://brightspot.com, Brightspot creates the robots.txt file at https://brightspot.com/robots.txt.
To customize a site's robots.txt:
- Click > Admin > Sites & Settings.
- In the Sites widget, select the site for which you are configuring
robots.txt, or select Global to configurerobots.txtfor all sites. - Click , located to the left of , and type
robots.txt. - In the robots.txt field, enter directives for the search engine. See the search engine's documentation for the list of honored directives.
- Click Save.
See also:
- Introduction to robots.txt
- How Google interprets the robots.txt specification
- Overview of Google crawlers and fetchers (user agents)
JSON-LD
JSON-LD objects provide a structured form to your assets that may provide better rankings in internet searches.
Motivation
A typical result from an internet search includes a page's title, text containing the search terms, and possibly an image.

Other components are implied in search results, even though visitors do not see them. For example, publication date is an implied component, because search engines often allow filtering for assets published within the past six months.
A page's HTML may contain all of the components that a search engine needs to provide meaningful search results; often, however, those components are difficult to parse out of the HTML code itself. Even worse, the components may be missing from the HTML, and the search engine needs to infer or guess them.
JSON-LD addresses this chaos by folding a page into a predictable structure. A JSON-LD object clearly identifies the asset's title, body, when it was original published, most recently published, and much more.
1{2"@context": "http://schema.org",3"@graph": [{4"@type": "Article",5"articleBody": "In this webinar, we'll discuss these challenges along with how businesses can utilize a digital asset management (CAM) system to overcome them.",6"datePublished": "2022-03-18T15:38:04.292Z",7"dateModified": "2022-03-18T15:55:54.824Z",8"headline": "Overcoming 4 common digital asset management challenges"9}]10}
The previous snippet is an example of a JSON-LD object corresponding to the above search result. (The actual JSON-LD object is quite a bit longer.) When a search engine detects a JSON-LD object inside a web page, it crawls that object instead of the HTML.
For a full description of JSON-LD, see JSON-LD JSON for Linking Data.
Benefits
Search engines use JSON-LD to include more attractive information about your assets in their results. The following are examples of presentations that Google applies when reading JSON-LD.
Rich results
Rich results provide a preview of the entire asset directly inside search results.
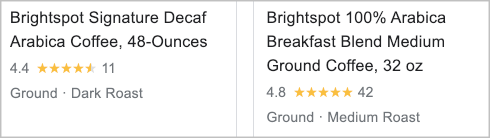
Product reviews
Google aggregates product reviews from various sources, and summarizes them inside the search results.
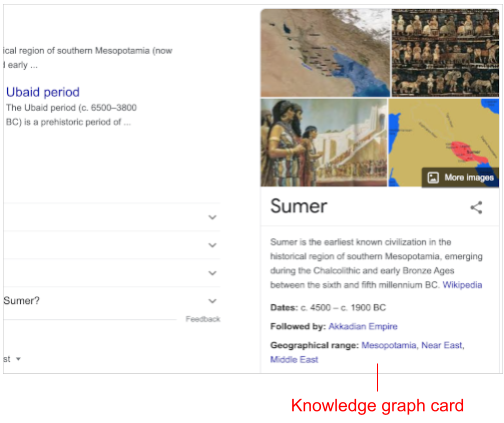
Knowledge graph cards
Knowledge graph cards appear to the right of search results.
The following resources provide additional information about JSON-LD.
- Understand how structured data works
- Explore the search gallery
- How Does Google Reward You for Using JSON-LD?
Configuration
For every asset that you publish, Brightspot can generate and deliver a JSON-LD object with several types of @graph entries, such as Organization and Website. The following procedure describes how to enable and customize the generation of those JSON-LD objects.
To configure JSON-LD generation:
- Click > Admin > Sites & Settings.
- In the Sites widget, select the site for which you want to enable JSON-LD, or select Global to enable JSON-LD for all sites.
- Click , located to the left of , and type
JSON-LD. - From the Organization list, select Set.
- Using the following table as a reference, complete the fields as needed.
- Click Save.
Brightspot adds the JSON-LD object to assets you subsequently publish.
You can view an published JSON-LD object by viewing a page's source and searching for <script type="application/ld+json">.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter a site name, or retain the default site name configured in Main > Name. Brightspot uses this name in various name attributes. |
| URL | Enter the site's URL, or retain the default. Brightspot uses the URL to construct various attributes, such as url and @id. |
| Website Description | Enter a description. Brightspot uses this description for the description attribute in the object "@type": "Website". |
| Logo | Select an image. Brightspot uses this image's URL in the logo/url attribute. |
| Social Links | List of URLs to your social media accounts. Brightspot adds these URLs to the sameAs attribute. |
See also: