Audiences
You can deliver different variations of an asset to different audiences. For example, you can deliver one version of a news story on a weekday, and a different version on a weekend.
You characterize audience segments by the following characteristics:
- Content type, such as articles or images
- Target, such as device, day of week, and cookies
- Site
When a visitor requests an asset, Brightspot checks the associated content type, target, and site, and then delivers the corresponding variation. If the visitor's request does not fall into one of the segments, Brightspot delivers the default variation.
Creating audiences
This topic explains how to create an audience in Brightspot.
To create an audience:
- Click > Admin > Audiences.
-
In the Name field, enter a name that reflects the audience you are defining. For example, Weekend Visitors reflects an audience that views content on weekends.
-
In the Content Type Group field, click .
-
In the content picker, click New Content Type Group.
-
In the content edit page, do the following:
- In the Name field, enter a name for the content type group, such as
Landing Pages. - From the Types list, select the content types that you want to apply to this audience.
- Click Save.
- Click Back.
- In the Name field, enter a name for the content type group, such as
-
From the Content Type Group list, select the content type group that you just created.
-
Do one of the following:
- Under Sites, click and select a site to which the audience applies. Repeat to add additional sites.
- Toggle on Enable On All Sites to activate this audience on all sites.
For an explanation of these settings, see the following table "Effect of adding audiences to sites."
-
Under Targets, and using the following table "Audience target types" as a reference, set one or more targets.
-
Click Save.
You can now create variations for the audience; for details, see Creating audience variations.
The following table describes the interaction between associating an audience with explicit sites and the Enable On All Sites toggle.
Effect of adding audiences to sites:
The Enable On All Sites toggle and site specification interact as follows:
- When sites are specified and Enable On All Sites is toggled ON: Audience applies to all sites
- When sites are specified and Enable On All Sites is toggled OFF: Audience applies only to specified sites
- When no sites are specified (regardless of toggle state): Audience applies to all sites
The following table describes the available target types.
Audience target types:
-
Cloud Front Device Category Target - Variation depends on the visitor's device as detected by Amazon's CloudFront service. Use only for CloudFront deployments.
-
Cookie Target - Variation depends on cookies set in a visitor's browser. Cookies typically define a visitor's characteristics, such as preferred language or time zone.
-
Day of Week Target - Variation depends on one or more specified days.
-
Device Category Target - Variation depends on the visitor's device, such as phone or tablet. For CloudFront deployments, use the Cloud Front Device Category target instead.
-
Header Target - Variation depends on values in HTTP headers.
-
Parameter Target - Variation depends on the key-value pairs in an item's query string.
-
Subscription Plan Target - Variation depends on the subscription plan selected. Each audience can contain multiple subscriptions. Should only apply to authenticated users with the corresponding subscription plan.
-
Tagged Content View Count Target - Variation depends on meeting these criteria: requested item is of a specified content type, visitor has previously viewed items of a particular content type with a specified tag, and visitor viewed those items a minimum number of times (optionally during a specified time). This target applies only to sites with authenticated users. For more information, see Tagged content view counts and Type view count target.
-
Tealium Target - Variation depends on audiences imported from Tealium. For more information, see Creating audiences using Tealium targets.
-
Theme Target - Variation depends on the site's theme.
-
Type View Count Target - Variation depends on meeting these criteria: requested item is of a specified content type, visitor has previously viewed items of a particular content type, and visitor viewed those items a minimum number of times (optionally during a specified time). This target applies only to sites with authenticated users. For more information, see Creating audiences using Tealium targets.
Modifying audiences
This topic explains how to modify audiences that you have already created in Brightspot.
To modify an audience:
- Click > Admin > Audiences.
- Click the audience you want to modify.
- Modify the settings as required. For details, see Creating audiences.
- Click Save.
Archiving audiences
This topic explains how to archive audiences that you have created in Brightspot.
To archive an audience:
- Click > Admin > Audiences.
- Click the audience you want to delete.
- Click Archive.
Tagged content view counts
You use this target when you want to deliver a variation if a visitor has already viewed items of a particular content type that have a particular tag. For example, you define the following criteria:
- Content type group is
Homepage - Previously viewed content type is
Article - Previously viewed articles were tagged with
Community - Minimum count is set to five
The interpretation of this target is that after a visitor views five articles tagged with Community, Brightspot delivers the corresponding variant of all content types associated with Homepage.
Type view count target
You use this target when you want to deliver a variation if a visitor has already viewed items of a particular content type. For example, you define the following criteria:
- Content type group is
Homepage - Previously viewed content type is
Article - Minimum count is set to five
The interpretation of this target is that after a visitor views five articles, Brightspot delivers the corresponding variant of all content types associated with Homepage.
Creating audience variations
You can create variations of assets for different audiences. Examples of audience variations include:
- Short articles for weekday visitors, long articles for weekend visitors.
- US spelling, UK spelling.
- Domestic readers, international readers.
To create audience variations:
-
Publish a new asset or open an existing one. Ensure the asset is one of the content types you used when creating an audience as described in Creating audiences. This is the default variation, and Brightspot delivers this variation to all visitors who do not satisfy any of the audience segmentation criteria.
-
From the audience list, select an audience for which you want to create a variation.
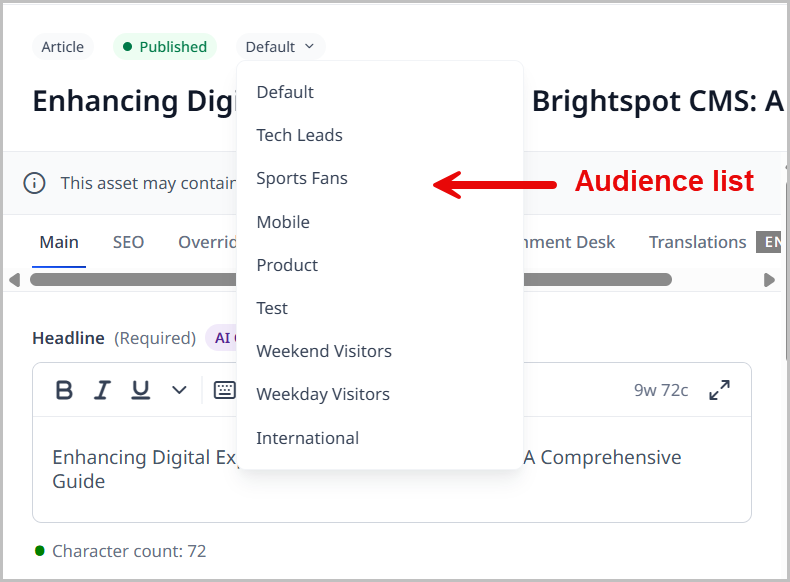
-
(Optional) Click the link in the message area to view the audience's description.
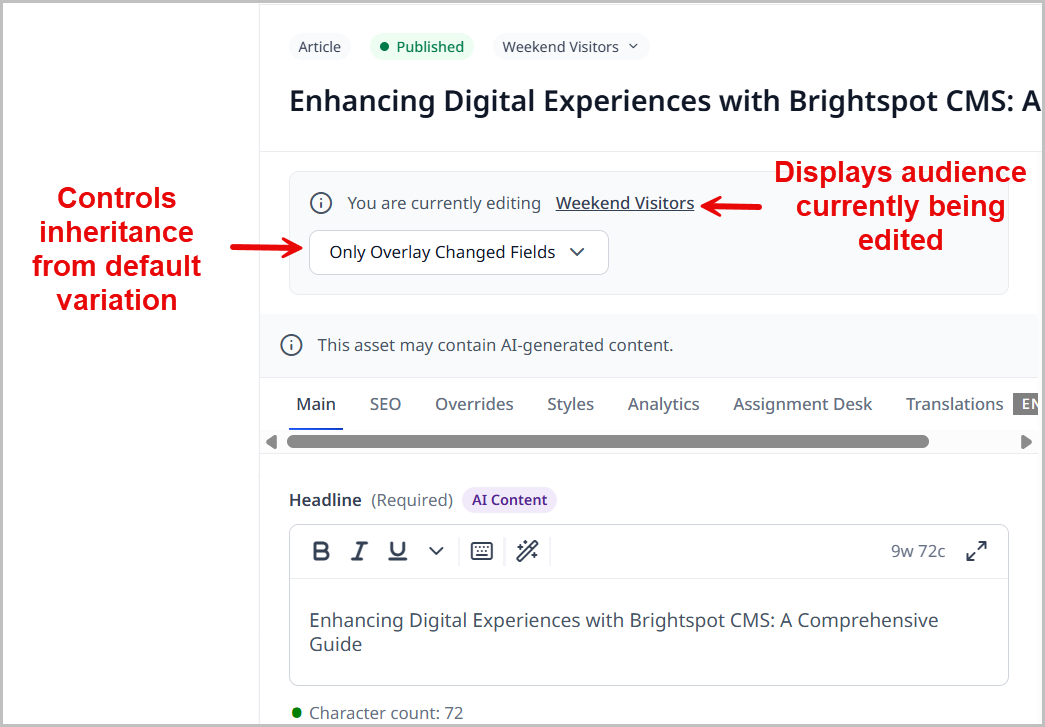
-
From the list box, select one of the following:
- Only Overlay Changed Fields—Any changes you make in the default variation flow to this variation except for those fields you modify in this variation.
- Overlay All Fields—No changes you make in the default variation flow to this variation.
For more information about controlling variation inheritance, see Understanding variation inheritance.
-
Complete your site's workflow and publish the variation.
Previewing audience variations
You can preview audience variations in the preview pane.
To preview asset variations:
-
Search for and open the asset whose audience variations you want to preview.
-
From the audience list, select the audience whose variation you want to preview.
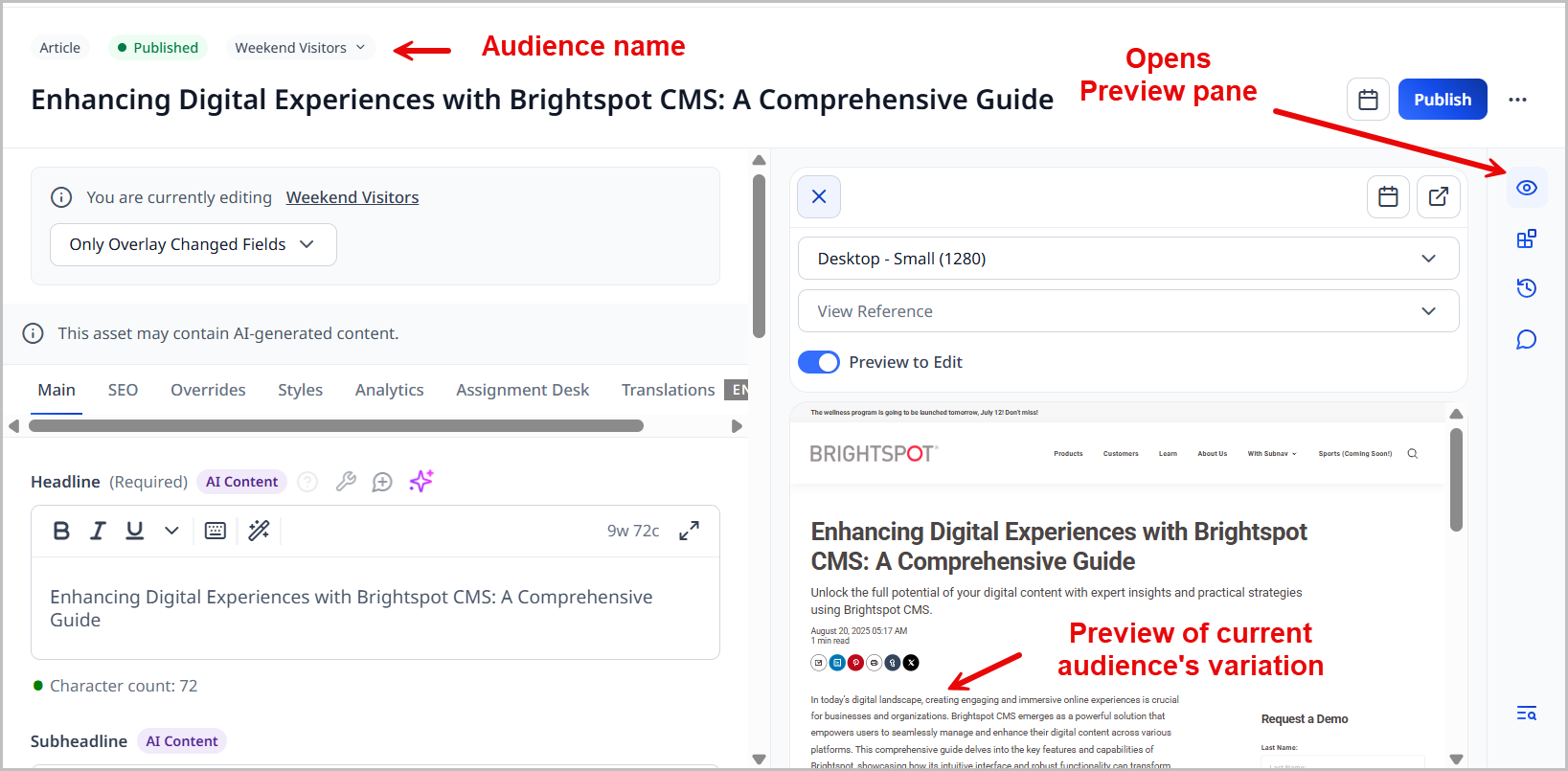
-
If the preview pane is closed, click to open it.
-
Select a different audience to view its variation in the preview pane.
Understanding variation inheritance
Some publications create variations of assets for different audiences, such as an article for US audience and a variation of that article for an international audience. Brightspot uses inheritance to manage the content between audience variations. (For other examples of audience variations, see Creating audience variations.)
-
When you start a new audience variation, its fields inherit content from the default variation.
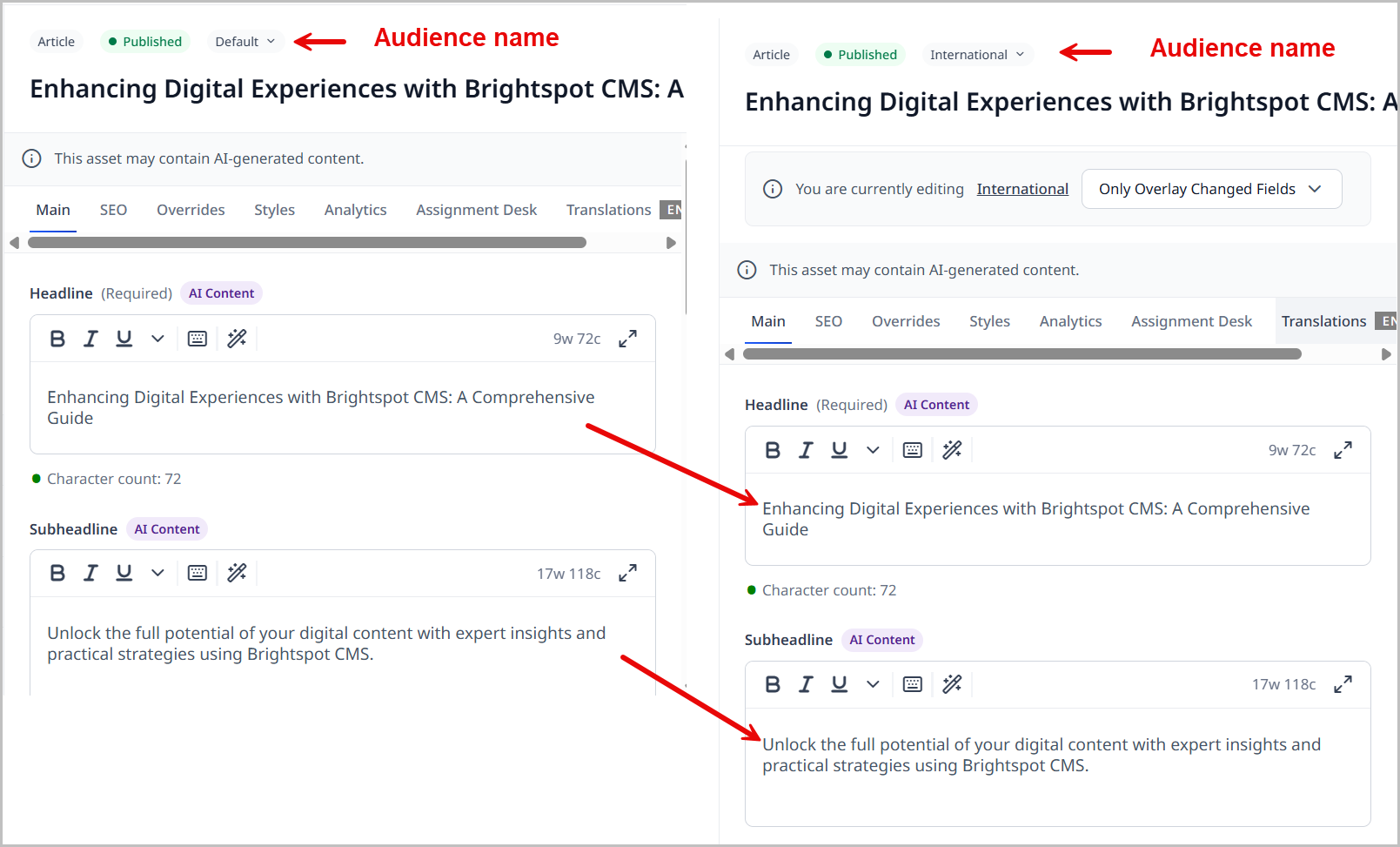
-
When you modify fields in the default variation, those changes cascade to the corresponding fields in the audience variation. The cascading stops when one of the following is true:
- You changed a field in the audience variation. Brightspot protects such changes from being overwritten from the default variation.
- You intentionally canceled the inheritance from the default variation as described in Creating audience variations.
Example 1: Text flow for unchanged fields
Adam Braun is responsible for delivering assets to native English speakers as well as to an international audience. In the default variation for native speakers, he uses idioms; in the international variation, he uses standard wording. He also wants to keep the audience variation as current as possible by allowing cascading changes from the default variation.
Adam is currently working on an article about migrating a publication from print to digital. The default variation has a headline and subheadline. The phrase doubling down is an idiom that may not be familiar to international speakers, so Adam makes a variation of this asset for his international audience. When he initially creates the international variation, the wording flows from the default variation.
Default variation, first version:

International variation, initial draft:

He then changes the international variation's headline from Doubling down on digital transformation to Pursuing a digital transformation.

Back in the default variation, he modifies the headline. Because Adam changed the headline in the international variation, the inheritance from the default variation in that field is disconnected. Back in the international variation, the headline no longer cascades from the default variation.
Default variation, second version:

International variation, second version:

Next, in the default variation, Adam rewords the subheadline to include the keyword CMS. Because Adam did not change the subheadline in the international variation, the link to that field is still live with the default variation. His change in the subheadline cascades.
Default variation, third version:

International variation, third version:

Example 2: Blocking all variation inheritance
In another scenario, Adam publishes default and international variations, but the audiences are so disparate that he wants to avoid changes in the default variation from cascading. (For information about blocking variation inheritance, see Creating audience variations.)
For the default variation, he creates a headline and subheadline. He then starts an international variation, which initially inherits text from the default variation.
Default variation, initial version:

International variation, initial draft:

Adam returns to the default variation to make an update to the headline and subheadline fields. Adam views the international variation. Because all inheritance is blocked, neither the headline nor the subheadline change.
Default variation, second version:

International variation, second version:
