Content edit widgets
Content edit widgets are widgets that appear on an editor’s content edit page. Brightspot comes with standard widgets such as Revisions and URLs. You can also create your own custom content edit widgets, and you can configure the standard and custom content edit widgets.
Creating content edit widgets
You can create widgets that appear in the content edit page by extending the abstract class ContentEditWidget. That abstract class includes three abstract methods that you must override, all of which support displaying read-only data.
The following snippet shows an entire class for displaying the custom widget Current Time Zones in the content edit page. The custom widget lists several cities and their current time.
1import com.psddev.cms.tool.*;23①public class CurrentTimesWidget extends ContentEditWidget {45@Override6public void display(ToolPageContext page, Object content, ContentEditWidgetPlacement placement) throws IOException {7②Map<String, String> timeZoneIdentifiers = new HashMap<>();8timeZoneIdentifiers.put("New York", "America/New_York");9timeZoneIdentifiers.put("Los Angeles", "America/Los_Angeles");10timeZoneIdentifiers.put("Mexico City", "America/Mexico_City");1112page.writeStart("table");1314③page.writeStart("tr");15page.writeStart("th");16page.writeHtml("City");17page.writeEnd(); /* th */18page.writeStart("th");19page.writeHtml("Time");20page.writeEnd(); /* th */21page.writeEnd(); /* tr */2223④for (String myTimeZone : timeZoneIdentifiers.keySet()) {24page.writeStart("tr");25page.writeStart("td");26page.writeHtml(myTimeZone);27page.writeEnd(); /* td */28page.writeStart("td");29String localTime = displayTime(timeZoneIdentifiers.get(myTimeZone));30page.writeHtml(localTime);31page.writeEnd(); /* td */32page.writeEnd(); /* tr */33}34page.writeEnd(); /* table */35}3637⑤public ContentEditWidgetPlacement getPlacement(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {38return ContentEditWidgetPlacement.BOTTOM;39}4041⑥public String getHeading(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {42return "Current Times";43}4445private String displayTime(String timeZoneIdentifier) {46/*47Returns local time in hh:mm format based on48passed time zone identifier.49*/50}51}
- ①Declares the class
CurrentTimesWidget. Objects instantiated from this class appear as Current Times Widget in the content edit page. - ②Instantiates a HashMap of time zones.
- ③Writes a table header in the widget’s body.
- ④Loops through each time-zone record. For each record, call the method
displayTimeto retrieve and then print the time zone’s current time. - ⑤Positions the widget under the content edit form. For details about positioning a widget on the content edit form, see Position.
- ⑥Displays the widget’s heading.
Based on the previous snippet, the custom widget Current Times appears at the bottom of the content edit page.
Creating content edit widgets that update
The content edit page includes an updating URLs widget that contains traditional HTML form tags such as <textarea> and <select>. You can create custom updating widgets that provide web forms in the content edit page by extending UpdatingContentEditWidget—an abstract class that includes the abstract method displayOrUpdate you must override in addition to the abstract methods described in Creating content edit widgets. These widgets respond to events and instantiate custom objects for data validation and posting content to the database.
In the following example you create a widget for attributing an article to a reporter—a typical task in a ghost-writing scenario.
Step 1: Create reporter model
In this step, you create a simple model to hold reporters’ first and last names.
1①public class Reporter extends Content {23private String firstName;4private String lastName;56/* Getters and setters */78②public String getFullName() {9return getFirstName() + " " + getLastName();10}11}
- ①Declares the class
Reporterthat extends fromContent. In a more robust implementation, you might create the classReporterthat extends ToolUser, create the classReporterRolethat extends ToolRole, and then assign instances ofReportertoReporterRole. - ②Returns a reporter’s full name as a concatenation of the reporter’s first and last name.
Step 2: Add field to model, hide from content edit form
By default, Brightspot places all of a model’s fields in the content edit form. In this example, you are attributing an article to a reporter, so a reporterCredit field must be part of the article’s model. Because reporterCredit appears in an updating content edit widget, you must use the @ToolUi.Hidden annotation in the model to remove the field from the content edit form.
1public class Article extends Content {23@ToolUi.Hidden4private Reporter reporterCredit;56public Reporter getReporterCredit() {7return reporterCredit;8}9}
Step 3: Display custom updating widget in content edit page
1import com.psddev.cms.tool.ContentEditWidgetPlacement;2import com.psddev.cms.tool.ToolPageContext;3import com.psddev.cms.tool.UpdatingContentEditWidget;4import com.psddev.dari.db.Query;5import content.article.*;67①public class ReporterCreditWidget extends UpdatingContentEditWidget {89@Override10②public void displayOrUpdate(ToolPageContext page, Object content, ContentEditWidgetPlacement placement) throws IOException {1112③Article myArticle = (Article) content;1314④if (placement == null) {15⑤UUID reporterID = page.param(UUID.class, "reporter.select");16⑥Reporter creditedReporter = Query.from(Reporter.class).where("id = ?", reporterID).first();17⑦myArticle.setReporterCredit(creditedReporter);18return;19}2021⑧List<Reporter> reporters = Query.from(Reporter.class).selectAll();22⑨Reporter currentReporter = myArticle.getReporterCredit();2324⑩page.writeStart("select", "name", "reporter.select");25page.writeStart("option", "value", "").writeEnd(); /* Initial blank option */26for (Reporter reporter : reporters) {27page.writeStart("option", "selected", reporter.equals(currentReporter) ? "selected" : null, "value", reporter.getId());28page.writeHtml(reporter.getFullName());29page.writeEnd(); /* option */30}31page.writeEnd(); /* select */32}3334@Override35⑪public ContentEditWidgetPlacement getPlacement(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {36return ContentEditWidgetPlacement.RIGHT;37}3839@Override40⑫public String getHeading(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {41return "Reporter Credit";42}4344@Override45⑬public boolean shouldDisplay(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {46return content instanceof Article;47}48}
- ①Declares the class
ReporterCreditWidgetas a subclass of an updating content widget. - ②Callback for displaying or updating a content edit widget.
- ③Casts the incoming asset as an
Article. - ④Traps the widget’s update event.
- ⑤Retrieves the selected reporter’s UUID.
- ⑥Retrieves the
Reporterrecord matching the selected reporter’s UUID. - ⑦Assigns the retrieved reporter record to the article.
- ⑧Retrieves all of the reporters.
- ⑨Retrieves the current article’s reporter credit.
- ⑩Renders the widget's bgody with an HTML
<select>field. The field’s options are a default blank entry and the list of retrieved reporters. - ⑪Positions the widget in the right rail.
- ⑫Displays the widget’s heading Reporter Credit.
- ⑬Displays the widget if the current content type is an article.
Based on the previous snippet, the custom updating content widget Reporter Credit appears in the right rail of the content edit page.

Position
The position of a widget refers to its location relative to other widgets with the same placement. The following sections describe Brightspot’s default positioning logic as well as techniques for overriding that logic.
Default positioning
Within the same Placement (top, bottom, right, dedicated tab), Brightspot by default positions custom widgets in alphabetical order based on the class’s fully qualified name. For example, suppose you defined three custom widgets, widgets.AdamsCustomWidget, widgets.JacksCustomWidget, and specials.widgets.ZoesCustomWidget, and all of them appear under the content edit form. By default, Brightspot positions them in alphabetical order as in the following illustration.
Custom positioning
You can override the alphabetical sorting for custom widgets by implementing the method ContentEditWidget#getPosition and returning a double value. Values with smaller numbers appear closer to the top, and the default value is zero. Positions with the same value are sorted alphabetically by fully qualified class name.
1import com.psddev.cms.tool.ContentEditWidget;2import com.psddev.cms.tool.ContentEditWidgetPlacement;3import com.psddev.cms.tool.ToolPageContext;45public class JillsCustomWidget extends ContentEditWidget {67@Override8①public ContentEditWidgetPlacement getPlacement(ToolPageContext toolPageContext, Object o) {9return ContentEditWidgetPlacement.BOTTOM;10}1112@Override13②public double getPosition(ToolPageContext page, Object content, ContentEditWidgetPlacement placement) {14return 8.0;15}1617@Override18public String getHeading(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {19return "Jill's Custom Widget";20}2122@Override23public void display(ToolPageContext page, Object content, ContentEditWidgetPlacement placement) throws IOException {24page.writeStart("p");25page.writeHtml("Here is Jill's custom widget.");26page.writeEnd();27}28}
- ①Places Jill’s widget under the content edit form.
- ②Assigns Jill’s widget a relative position of 8.0
Suppose you assign Zoe’s, Adam’s, Jack’s, and Jill’s widgets return values for getPosition as in the following table.
Example values for positioning widgets
| Widget | Fully Qualified Class Name | getPlacement | getPosition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zoe | special.widgets.ZoesCustomWidget | ContentEditWidgetPlacement.BOTTOM | 10.0 |
| Adam | widgets.AdamsCustomWidget | ContentEditWidgetPlacement.BOTTOM | 10.0 |
| Jack | widgets.JacksCustomWidget | ContentEditWidgetPlacement.BOTTOM | 8.0 |
| Jill | widgets.JillsCustomWidget | ContentEditWidgetPlacement.BOTTOM | 9.0 |
Because all the widgets have the same placement, Brightspot lays them out as in the following illustration.
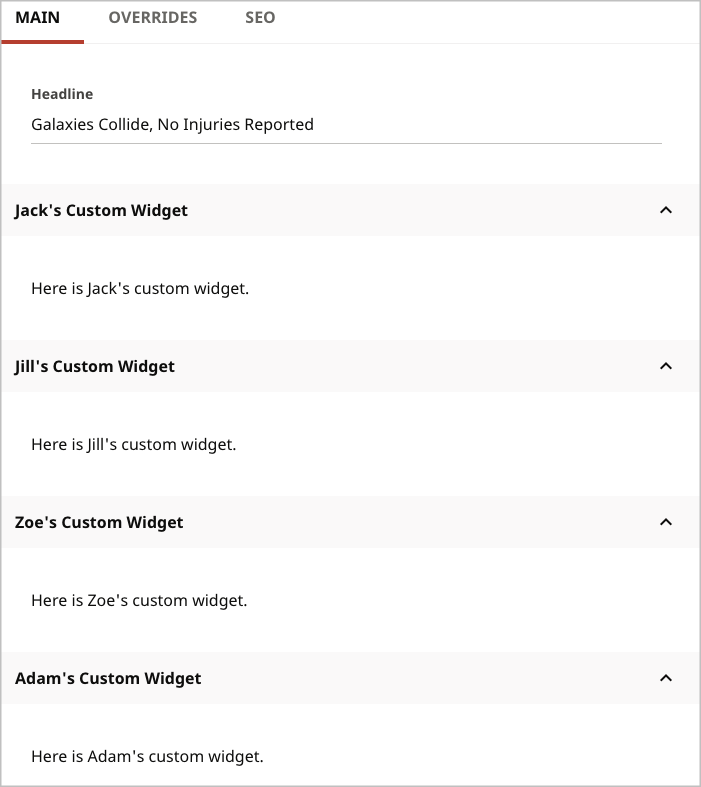
Both Zoe’s and Adam’s widgets have the same return value for getPosition, so Brightspot breaks the tie by sorting by fully qualified class name.
Custom positioning with substitution
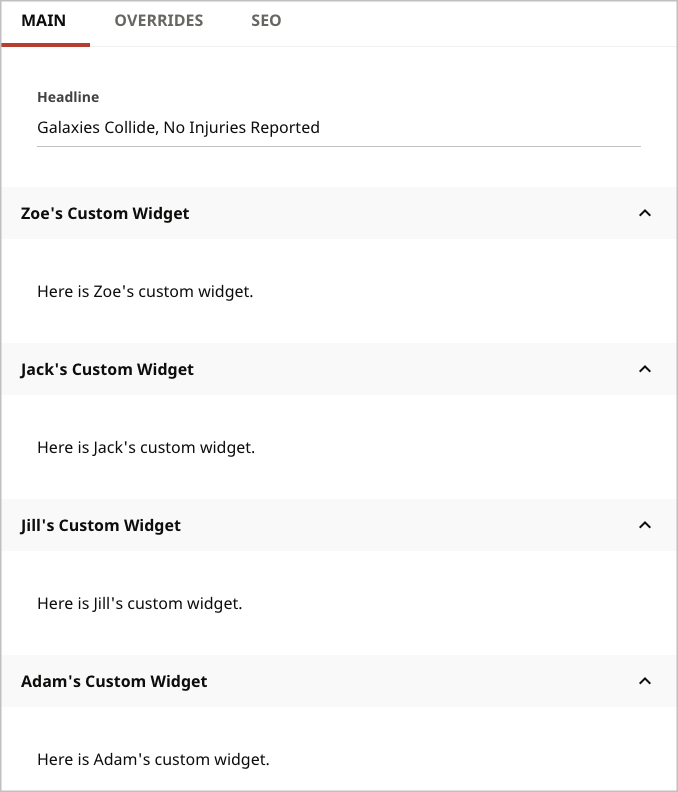
If you use a custom widget that is imported from another package, that widget may have a result from getPosition that conflicts with your implementation. Referring to the table "Example values for positioning widgets," Zoe’s custom widget has a position of 10, but you may want to place her widget first, in front of all the other custom widgets.
You can use substitutions to incorporate an imported widget into your project and then override the original value for getPosition.
At run time, the ported custom widget appears first among all other custom widgets under the content edit form.
1import com.psddev.cms.tool.ContentEditWidgetPlacement;2import com.psddev.cms.tool.ToolPageContext;3import com.psddev.dari.db.Substitution;4①import special.widgets.ZoesCustomWidget;56②public class ZoesPortedCustomWidget extends ZoesCustomWidget implements Substitution {78@Override9③public double getPosition(ToolPageContext page, Object content, ContentEditWidgetPlacement placement) {10return 6.0;11}1213}
- ①Imports the custom widget
ZoesCustomWidgetfrom another package. - ②Declares a ported custom widget
ZoesPortedCustomWidgetby extending the imported custom widget and implementingSubstitution. - ③Overrides the imported widget’s position, now assigning it 6 (compared to the original 10 as listed in the table "Example values for positioning widgets"). This position value is the lowest of all other custom widgets.
At run time, the ported custom widget appears first among all other custom widgets under the content edit form.
Placement
The placement of a widget refers to its location relative to the content edit form: top, bottom, right, or in its own tab. You provide a placement for a custom widget by implementing the method ContentEditWidget#getPlacement.
1public ContentEditWidgetPlacement getPlacement(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {2/* Return one of the placement constants. */3}
See the snippet "Implementing a custom widget in content edit page" for an implementation of this method.
The following table lists the available placement constants.
Placement constants
| Constant | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
TOP | Places widget above content edit form. | return ContentEditWidgetPlacement.TOP; |
TAB | Places widget in its own tab. If you use this position, the tab does not appear for embedded objects in the content edit form. | return ContentEditWidgetPlacement.TAB; |
BOTTOM | Places widget below content edit form. | return ContentEditWidgetPlacement.BOTTOM; |
RIGHT | Places widget below URLs widget. | return ContentEditWidgetPlacement.RIGHT; |
Hiding
By default, Brightspot displays the following standard widgets in the content edit page: References, Revisions, SEO, Sites, Template, and URLs. Some of these widgets appear depending on an item’s state. For example, the Revisions widget appears only after you save a draft, change a workflow state, or publish an item. In addition, Brightspot automatically displays any custom widgets created for the content edit page. (For information about creating custom widgets for the content edit page, see Creating content edit widgets and Creating updating content edit widgets.)
You can hide widgets at the content-type level and at the custom widget level.
Hiding widgets at the content-type level
You can hide the standard or custom widgets at the content-type level. For example, you can show the URLs widget on content edit pages for articles, and hide the widget on content edit pages for images.
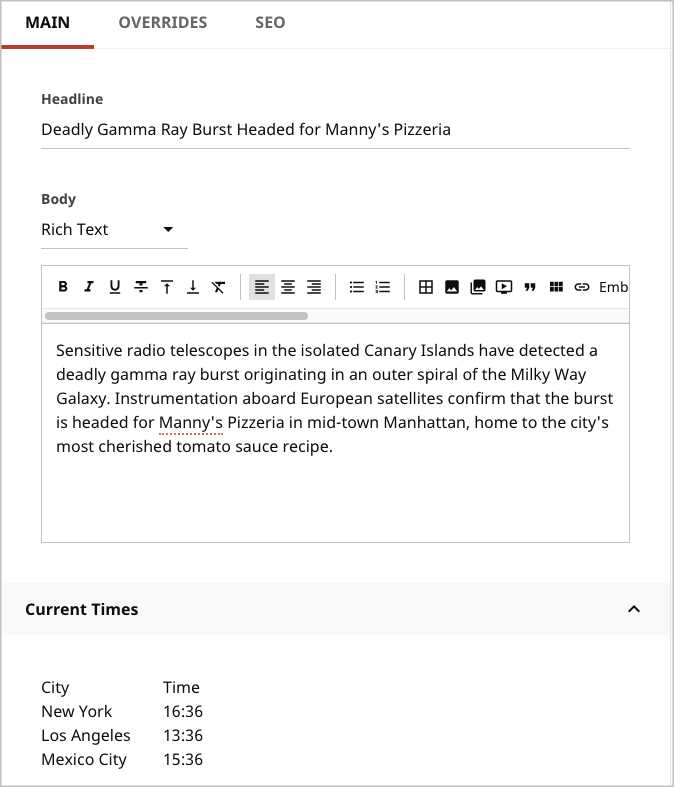
The interface ContentEditWidgetDisplay contains a method shouldDisplayContentEditWidget that you can override to specify if a widget is visible or not in a content edit page. You implement the interface at the model level, which gives you the flexibility for showing or hiding widgets depending on content type. The following example shows how to hide the standard URLs widget in an article’s content edit page.
1import com.psddev.cms.db.Content;2import com.psddev.cms.db.ToolUi;3import com.psddev.cms.tool.ContentEditWidgetDisplay;4import com.psddev.cms.tool.content.UrlsWidget;5import com.psddev.dari.db.Recordable;67public class Article extends Content implements ContentEditWidgetDisplay {89@Recordable.Required10private String headline;1112@ToolUi.RichText13private String body;1415@Override16①public boolean shouldDisplayContentEditWidget(String widgetName) {17if (widgetName.equals(UrlsWidget.class.getName())) {18return false;19} else {20return true;21}22}23}
- ①Implements the method
shouldDisplayContentEditWidget. Brightspot calls this method for each widget eligible to appear in the content edit page. If the widget’s name is the same as the URLs widget’s name, the method returnsfalseand the widget does not appear. See the following illustration.

Hiding custom widgets
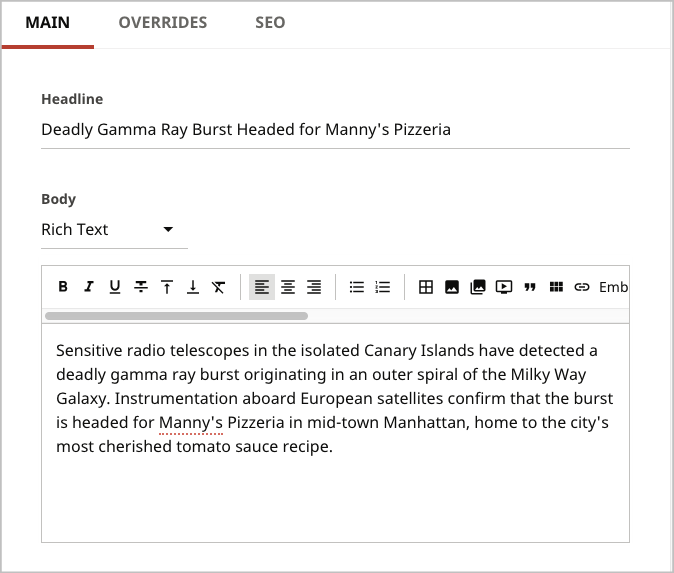
If you create a custom widget, you can hide it from the content edit page—regardless of the content type—by overriding the shouldDisplay method in the widget’s definition.
1import com.psddev.cms.tool.ContentEditWidget;2import com.psddev.cms.tool.ContentEditWidgetPlacement;3import com.psddev.cms.tool.ToolPageContext;45public class CurrentTimesWidget extends ContentEditWidget {67@Override8①public void display(ToolPageContext page, Object content, ContentEditWidgetPlacement placement) throws IOException {910page.writeStart("p");11page.writeHtml("My widget for personal notes.");12page.writeEnd(); /* p */13}1415public ContentEditWidgetPlacement getPlacement(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {16return ContentEditWidgetPlacement.BOTTOM;17}1819public String getHeading(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {20return "My Custom Widget";21}2223@Override24②public boolean shouldDisplay(ToolPageContext page, Object content) {25return false;26}27}
- ①Defines a custom widget that appears under the content edit form.
- ②Hides the custom widget from the content edit page. See the following examples.
 |  |
|---|
Additional configuration
You can configure widgets on the content edit form directly from Brightspot. Configuration includes the following features:
- Creating custom content edit form by content type.
- Assigning custom content edit forms at the role level or to site-role combinations.
- Add tabs to content edit forms, and adding fields to those tabs.
- Assigning read/write permissions at the tab and field level.
For details about these configuration activities, see the following topics in the Editorial Guide: